In ‘Flying solo’ this time around, Sue Littleford sets out why we should always consider training and CPD a vital cog to keep the wheels of our business turning.
Huh? A business asset? Training and continuing professional development? Well, yes, that’s exactly what it is. And as with the acquisition of any asset for your business, it’s something you should approach with deliberation.
If anything will bear a cost–benefit analysis for a sole trader or other small business, it’s the investment of your time and money in refreshing and developing skills and learning new ones. So let’s take a look, first, at the benefit side of that equation.
The benefits of training and CPD
- Knowing what you’re doing: investing in your training, rather than relying merely on having a good grasp of spelling, punctuation and grammar, is one of the principal ways to keep imposter syndrome at bay. You will know you know what you’re doing.
- Marketing: when you’re confident that you know what you’re doing, it’s so much easier to market yourself and to craft robust CV and website text. Ayesha Chari demonstrated this beautifully when she wrote her out-of-office message before attending the 2023 CIEP conference: ‘I’m taking time off for CPD this month to raise my editing skills and business services for my clients!’ Clients do love a supplier who is up to date and investing in their skills, and I shall be brazenly stealing Ayesha’s idea!
- Upgrading: I’ve been to the upgrade Q&A at the last two CIEP conferences and know that training is absolutely key for upgrading, as is evidence of recent CPD to become an Advanced Professional Member, so lay the groundwork now, with a solid basis in the core skills (how to actually proofread and/or copyedit) as a launchpad for future needs when you niche down. No knowledge is ever wasted. And a Professional (or Advanced Professional) Member badge on your website, marketing materials and socials is a great selling point.
- Upgrading to at least Professional membership is not only a requirement for remaining in the CIEP beyond seven years, it also feeds into marketing as then you can take out an entry in the Directory, the go-to place to find an editor or proofreader for a huge range of clients. You can complete the training section of your Directory entry as another way of demonstrating to clients that you’ve invested in providing a good and knowledgeable service to them.
- Working efficiently and effectively: when you achieve this, you can improve the effective hourly rate you achieve in fixed-fee jobs, as well as feeling in control of your business.
The costs side of the equation
- As with any asset, you need to decide what it is you need to learn, where you’re going to source it from, and exactly which course from many offers to choose. When you’re spending your own money on training, rather than your employer’s, these decisions become acutely important.
- Budget time to do the course as well as the money to pay for it. It’s a waste if you buy a course then never find the time to do the learning. With self-directed courses, it’s far too easy to keep kicking that can down the road until access to the course is running out and you sprint through it far too quickly to get the most out of your investment.
- Besides the time spent on the course itself, also budget for time to elapse between courses. Allow yourself the chance to embed your learning, to practise those new skills and to make them your own. Filling your head with a cascade of new ideas to implement can lead to incoherence, overwhelm and, yes, imposter syndrome. Take a breather between courses.
- Plan: you can’t do everything; you certainly can’t do everything all at once. There’s a tab on the Training and CPD spreadsheet in the Going Solo toolkit (CIEP members only) to keep a wish list of courses you want to do. If you’re interested in learning more about a particular aspect of editing, then you can use that tab to keep a record of potential courses, and weigh up the pros and cons of doing each one.
- Go with reputable suppliers for the biggest marketing bang for your buck, and the best educational opportunities. I’ve seen some courses offer the world for £29.99, on websites where they have a distance-learning course for every topic under the sun. Don’t waste your £29.99 – they’re not tremendous value, they’re inadequate training. They will not take you from novice to accomplished editor in ten easy lessons.
- Where you can, prioritise courses that have some form of assessment, and tutor support. Checking your work against model answers is all very well, but properly supported training is invaluable when you’re getting your core skills under your belt. Such courses will take more effort on your part. Good! They’ll also impress clients more.
- Speaking of costs, in the UK not all training is tax-deductible. Training that keeps your skills up to date is an allowable business expense. Training that puts you in the position to begin trading, or extend your business into a new area, even if it’s a related one, is not.
- Record-keeping: back to the Going Solo toolkit for another tab: completed training. Keep a good record of the training you’ve taken and be ready for easier upgrading. The spreadsheet was designed with the upgrades process in mind – the Admissions Panel has approved it, so you can just send in your spreadsheet (trim it of the unnecessary tabs before you do) to save having to type out every editorial course you’ve ever done on the application form.
Never think you know it all
You don’t know it all. No one does. I know I don’t! There’s always more to learn in our ever-evolving field – that’s one of the joys of being an editor or proofreader!
I’m always disheartened when people say to me that there’s nothing more for them to learn, that they did one course, five years ago, so they’re ‘qualified’, and there’s nothing more they need to know. (Yes, I’ve really had people say that to me.)
There’s no ‘qualification’ per se in the editorial world. Graded membership, as in the CIEP, and Australia and New Zealand Aotearoa’s Institute of Professional Editors (IPEd), is pretty rare, and the best proxy for ‘qualification’. Other countries and other membership organisations have certification courses but this is not the same ‘qualified’ as a doctor, a lawyer or a civil engineer. No editor should be speaking of being ‘qualified’ in that sense. And qualified doctors, lawyers and civil engineers (among many others) have a requirement to evidence a minimum number of CPD hours each year to retain membership of their professional organisation.
Unless you keep abreast of what’s out there, you may not even know what you don’t know. Be curious – a key requirement for good editing. Read the CIEP’s Curriculum for professional development to see what else you might pursue and don’t forget training beyond editing if you’ve got a need for subject-specific learning, or, indeed, business-skills learning.
Which brings us to …
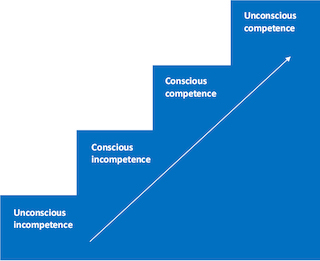
Unconscious incompetence to unconscious competence
I first came across the Hierarchy of Competence model in management training, many years ago, and I’ve since encountered the related Dunning–Kruger effect, which adds the idea that, to paraphrase heavily, in areas where we don’t realise what we don’t know, we are more likely to think we know rather more about it than we actually do.
Although it’s often presented now as a pyramid, when I first came across the Hierarchy of Competence model, it was shown as a staircase.
Unconscious incompetence is a happy place – you don’t know much, and you don’t realise just how little you know.
Conscious incompetence is a less happy place, but it’s a place of growth – you’re alerted to the fact that the thing you’re learning is actually bigger than you thought. Hopefully, though, it’s also an exciting place to be as you start to explore your new skills and milieu.
Conscious competence isn’t the happiest of places, either, but things are improving – you’re aware of how much you need to practise, and how much more there is to learn, but you’re getting used to wielding your skills and seeing results. It’s still all a bit of an effort, though.
Unconscious competence is great – you’re just getting on with the job and doing it well.
However, don’t think that this unconscious competence is the end of your learning journey. It does take some effort to stay there, or you’ll find yourself tumbling down the stairs as the landscape changes around you. That’s your cue to undertake CPD – emphasis on the C.
About Sue Littleford
Sue Littleford is the author of the CIEP guide Going Solo, now in its second edition. She went solo with her own freelance copyediting business, Apt Words, in March 2007 and specialises in scholarly humanities and social sciences.
 About the CIEP
About the CIEP
The Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP) is a non-profit body promoting excellence in English language editing. We set and demonstrate editorial standards, and we are a community, training hub and support network for editorial professionals – the people who work to make text accurate, clear and fit for purpose.
Find out more about:
Photo credits: header image by cottonbro studio, woman writing in a notebook by RF._.studio, love to learn by Tim Mossholder, all on Pexels.
Posted by Eleanor Smith, blog assistant.
The views expressed here do not necessarily reflect those of the CIEP.